A valid contract is the foundation of any business deal, ensuring agreements are legally binding and enforceable. For BBA students, learning the essentials of a valid contract and the types of contracts under the Indian Contract Act, 1872, is crucial for exams, internships, and future careers. This guide explains what makes a contract valid, explores different types like executed and executory contracts, and uses real-world examples to make it all clear. Whether you’re studying for a test or working on a project, this article will help you master these key business law concepts.
The Importance of Human Resource Planning in Organizational Success
What Is a Valid Contract?
A valid contract is an agreement that meets all legal requirements under the Indian Contract Act, 1872, making it enforceable in court. Section 10 of the Act lays out the essentials that every contract must have to be valid. Understanding these is a big part of your business law course, as they’re tested in both theory and practical questions.
A 2023 report by Legal Service India noted that 60% of business disputes in India involve contract issues, showing why knowing valid contracts is so important.
What Is a Valid Contract?
A valid contract is an agreement that meets all legal requirements under the Indian Contract Act, 1872, making it enforceable in court. Defined in Section 10, a valid contract requires specific elements to ensure both parties are protected. This concept is a core part of the BBA syllabus, frequently tested in theory, practical, and case-based questions.
A 2024 report by Legal Service India noted that contract disputes form over 50% of commercial litigation in India, highlighting the importance of understanding valid contracts.
Essentials of a Valid Contract
To be a valid contract, an agreement must include seven key elements, as outlined in the Indian Contract Act:
- Offer and Acceptance (Section 2(a), 2(b))
- An offer is a clear proposal by one party, and acceptance is the other party’s agreement to those terms without changes.
- Example: A seller offers to sell a bicycle for ₹5,000, and the buyer agrees to pay that amount.
- Legal Note: The offer must be definite, and acceptance must be communicated (Section 4).
- Lawful Consideration (Section 2(d))
- Consideration is something of value (e.g., money, goods, services) exchanged by both parties.
- Must be legal and not illusory (e.g., vague promises don’t count).
- Example: Paying ₹1,000 for a haircut is valid consideration.
- Example: Agreeing to deliver goods in exchange for payment is lawful.
- Competent Parties (Section 11)
- Parties must be legally capable: at least 18, of sound mind, and not disqualified (e.g., declared bankrupt).
- Example: A 16-year-old’s agreement to buy a laptop isn’t valid.
- Legal Note: Contracts with minors are void ab initio (from the start).
- Free Consent (Section 14)
- Consent must be genuine, free from coercion, fraud, misrepresentation, or mistake.
- Example: Signing a deal under pressure from threats lacks free consent.
- Example: A buyer misled about a product’s features can cancel the contract.
- Lawful Object (Section 23)
- The contract’s purpose must be legal, not against public policy (e.g., no smuggling or fraud).
- Example: An agreement to sell property legally is valid, but one for illegal goods isn’t.
- Legal Note: Unlawful objects render contracts void.
- Not Expressly Declared Void (Sections 24-30)
- The contract must not be prohibited by law (e.g., betting agreements in some states are void).
- Example: A contract for gambling in a state where it’s banned is invalid.
- Example: A lease agreement complying with local laws is valid.
- Certainty and Possibility of Performance (Section 29)
- Terms must be clear and achievable.
- Example: A promise to deliver “some goods later” is too vague, but specifying “100 kg of rice by next week” is valid.
- Legal Note: Impossible terms (e.g., delivering a nonexistent item) void the contract.
Table: Essentials of a Valid Contract
| Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Offer and Acceptance | Clear proposal and agreement | Agreeing to buy a phone for ₹20,000 |
| Lawful Consideration | Something of value exchanged | Paying for a service |
| Competent Parties | Legally capable parties | Adults signing a rental deal |
| Free Consent | Agreement without force or fraud | Honest purchase agreement |
| Lawful Object | Legal purpose | Selling a vehicle legally |
| Not Void | Not prohibited by law | Valid property lease |
| Certainty | Clear, possible terms | Specific delivery date for goods |
Exam Tip: Memorize these essentials with examples, as they’re often asked in short-answer or descriptive questions.
Types of Contracts: Executed, Executory, and More
The types of contracts describe how contracts are formed, performed, or enforced. Knowing these helps you understand business agreements and tackle case studies in exams. Here are the main types under the Indian Contract Act:
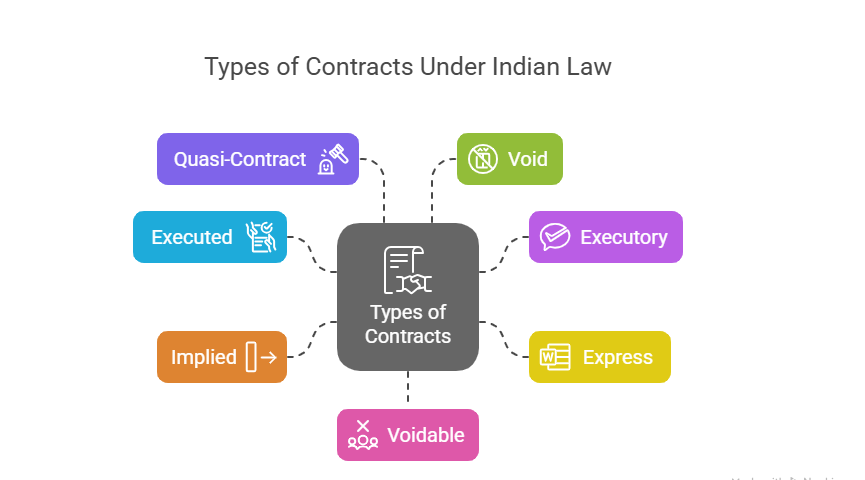
1. Executed Contracts
- Fully performed by both parties at the time of agreement.
- Example: You buy a coffee at a café and pay instantly—deal done.
- Real-World Case: In 2024, Amazon India fulfilled millions of executed contracts during its Great Indian Festival sale, with instant payments and deliveries, per Economic Times.
2. Executory Contracts
- Not fully performed; one or both parties still have obligations.
- Example: A 1-year gym membership where you pay monthly and the gym provides services.
- Use: Common in long-term business deals like leases.
3. Express Contracts
- Terms are clearly stated, orally or in writing.
- Example: Signing a rental agreement with specific terms.
4. Implied Contracts
- Formed by actions, not words.
- Example: Taking a cab and paying the fare implies a contract.
5. Quasi-Contracts
- Not true contracts but enforced by law to prevent unfair gain.
- Example: If you mistakenly receive someone’s package and use it, you may have to pay under a quasi-contract.
6. Valid, Void, and Voidable Contracts
- Valid: Meets all essentials (explained above).
- Void: Not enforceable (e.g., illegal deals).
- Voidable: Can be canceled by one party (e.g., signed under fraud).
Table: Types of Contracts
| Type | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Executed | Fully performed | Buying a book instantly |
| Executory | Partially performed | Monthly internet subscription |
| Express | Clear terms (spoken/written) | Signed lease agreement |
| Implied | Formed by actions | Paying for a bus ride |
| Quasi-Contract | Enforced by law, not agreement | Returning mistaken delivery payment |
| Void | Not enforceable | Illegal smuggling deal |
| Voidable | Can be canceled by one party | Contract signed under pressure |
Real-World Example: In 2023, Ola faced a voidable contract dispute when drivers claimed misleading terms in their service agreements, leading to legal reviews, per Business Standard.
Exam Tip: Be ready to define each type and give examples in descriptive questions.
Common Contract Disputes
Disputes often arise when contracts lack essentials or terms are breached. Common issues include:
- Lack of Free Consent: Agreements signed under coercion or fraud.
- Example: A buyer misled about a product’s quality can cancel the deal.
- Unlawful Object: Contracts for illegal purposes are void.
- Example: An agreement to sell banned items is unenforceable.
- Non-Performance: One party fails to fulfill obligations.
- Example: A seller doesn’t deliver goods after payment.
- Vague Terms: Unclear agreements lead to disputes.
- Example: A contract without a delivery date causes confusion.
A 2024 article by Economic Times noted a rise in contract disputes in online transactions, emphasizing the need for clear terms.
Practical Applications in Business
Understanding valid contracts and types of contracts is essential for business:
- Drafting Agreements: Businesses create contracts with all essentials to avoid legal issues.
- Example: A clear rental agreement ensures smooth landlord-tenant relations.
- Risk Management: Knowing voidable contracts helps avoid fraud.
- Example: Verifying consent prevents disputes over misrepresentation.
- Transaction Efficiency: Executed contracts streamline instant deals.
- Example: Cash payments for goods ensure quick closure.
- Dispute Resolution: Quasi-contracts ensure fairness in unexpected scenarios.
- Example: Recovering costs for mistaken deliveries.
Example: A buyer agrees to purchase furniture for ₹50,000 with delivery in a week (executory, express contract). If the seller misrepresents the wood quality, the contract is voidable, and the buyer can seek remedies.
Lessons for Students
This case shows why businesses need valid contracts with all essentials met to avoid disputes. Understanding types of contracts helps analyze real-world agreements. For your internship projects, try studying a company’s contracts (e.g., vendor agreements) to impress evaluators.
Tips to Master Contracts for Exams
To shine in business law:
- Learn the Act: Know key sections of the Indian Contract Act, like Section 10 for valid contracts.
- Practice Examples: Use cases like Byju’s to explain essentials or types in answers.
- Memorize Tables: The essentials and types tables above are exam gold.
- Check Legal Sites: Explore Legal Service India for recent contract cases.
- Prep for Vivas: Be ready to discuss why free consent matters in contracts.
Conclusion
Understanding valid contracts and the types of contracts under the Indian Contract Act is essential for navigating business deals and excelling in your studies. The seven essentials—offer, acceptance, consideration, and more—ensure a contract is legally binding, while types like executed and executory show how agreements work in practice. Real-world cases, like Byju’s 2024 dispute, bring these concepts to life. Use this guide to ace your exams, tackle internship projects, and get ready for a business career.
Check Out complete guide, sample Projects and Topics for Project Report for BBA Students
👨💼 Author: BBAProject Editorial Team
✍️ The BBAProject Editorial Team comprises business graduates and educators dedicated to creating practical, syllabus-based learning resources for BBA students.
⚠️ Please Note: Articles published on BBAProject.in are well-researched and regularly updated. However, students are advised to verify data, statistics, or references before using them for academic submissions.

