Market Segmentation is one of the 1st skills for BBA student to master in order to have a precise and powerful marketing strategy. By segmenting a market of many consumers into smaller subgroups with something in common, students can design campaigns that will appeal to specific people. And it’s something you will need in every academic project, internship or exam to prepare for a successful career in marketing. This guide examines the phenomenon of market segmentation, basic divisions and relevant uses, alongside practical recommendations on how to tackle sector problems, thus offering BBA students advice concerning developing their marketing skills.
Market Segmentation: The Base for Strategic Marketing
Market Segmentation is the practice of dividing a market into discrete groups (segments) consisting of consumers who have similar needs or purchase behavior traits. This strategy allows companies to concentrate their resources on targeted customer segments, offering personalized products and campaigns that generate loyalty and revenue. For retail management majors, learning market segmentation is important because these students need to know how to put together a marketing plan for such assignments as creating an ad campaign for a retailer that is trying to reach tech-savvy millennials. It also takes a substantial amount of space in the BBA course where we see it being used as a theory question (what are Segmentation categories) as well as practical viva’s (defend a campaign strategy).
For example, a student assigned to launch a new drink could segment the market in 18-24 year-olds to test whether an ad campaign focused on healthy and affordable drinks resonates with that stakeholder category. In internships, segmenting ability means the classmates can analyze customer data and make strategic promotion suggestions \xd0for example, pitching budget earphones to college students. Students who do well in this module will be able to target their resources more efficiently, improve the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and strengthen marketing planning.
Key Benefits for Students:
Good grades: Segmentation understanding aids in responding to exam questions and creating high scoring projects.
Implications for Application: Empowers students to develop data-driven projects in internships.
Professional Development: Ready students for marketing-analysis positions and campaign planning.
Core Categories of Market Segmentation
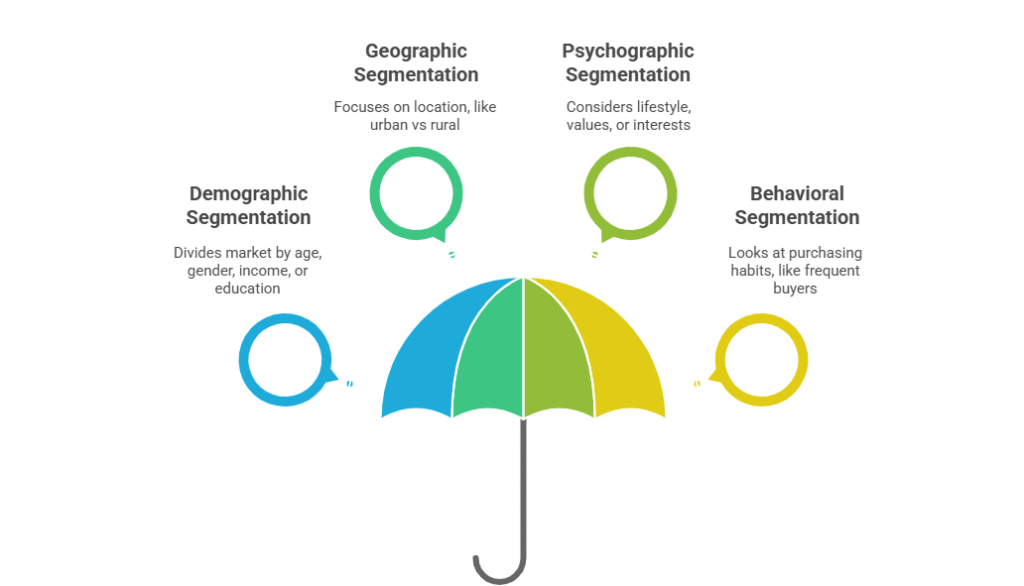
Market Segmentation is divided into four types main flow including characteristics of the customer. A knowledge of these classifications gives BBA majors the ability to devise targeted marketing plans for academic and real-world purposes.
Demographic Segmentation: Categorization of the market based on overall quantifiable characteristics like age, sex, income level, education level etc. For instance, a marketing plan designed by one student: she is planning to design her marketing plan for targeting young women aged 18-30 who would like to wear trendy affordable clothes. This classification technique is often used in practice because of its ease and efficiency.
Geographic Segmentation: Based on the customers’ locations including North, East, West, South and Urban vs. Rural areas etc. A college-age student may go after urban customers for a food delivery app, since smartphone usage is higher in cities.
Psychographic Segmentation: It focuses on the lifestyle, values or interests of customers. For example, a project could be aiming skincare products at consumers who care for the environment when making purchases.
Behavioral Segmentation -This analyses the behavior of the customer, their loyalty towards a specific brand, sensitivity in prices etc. A college student might angle for regular online shoppers who could receive exclusive discounts through a loyalty program.
Key Categories Table:
| Segmentation Type | Focus | Example | Syllabus Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | Age, gender, income | Budget phones for students | Marketing management |
| Geographic | Location | Umbrellas in rainy regions | Market analysis |
| Psychographic | Lifestyle, values | Eco-friendly bags for green consumers | Consumer behavior |
| Behavioral | Buying habits | Loyalty programs for frequent shoppers | Marketing strategy |
Strategic Application of Market Segmentation in Marketing Plans
Market Segmentation provides the foundation for business students to develop marketing strategies that can better meet customers’ needs. Through identifying key markets, students learn to create campaigns that raise awareness and provide measureable results. For instance, in a BBA project, students could segment a market into young professionals and develop a campaign for premium laptops that highlights considerations such as portability and performance. This way, the campaign hits home and raises project rating levels.
Segmentation is also the backbone of some very crucial marketing decisions such as product placement, price and promotion. For example, a student might employ behavioral segmentation to provide price-sensitive consumers with discounts that would grow sales by 15%. In internships, segmentation can allow students to work with real data, for example targeting rural customers for cheaper agricultural tools based on geographic data.
Example: A poll of 200 shoppers shows 70% are students and they like to use cheap, green products. A marketing proposal could develop cheap broken stuff and good hot air via some kind of social network engagement which would increase online interest by 25%.
Key Applications:
Targeted Campaign: Create ads that target particular segments (i.e., advertising exercising equipment to health-oriented demographics).
Product differentiation: Match products to needs of the segment (budget snack for students).
Pricing strategies: Price the offering according to segment affordability(rec, for example, cost of service to price-sensitive buyers).
Practical Steps to Implement Market Segmentation
In order to successfully use Market Segmentation in BBA projects and internships, students need adhere to the following plan:
Set Goals: Identify the objective of the project or task, like boosting sales for a retail brand.
Research: Utilize primary research (for example, interviewing 50 customers to understand age and preferences) and secondary research (such as an industry report demonstrating a jump in online shopping of 10%).
Segment the Market: Choose appropriate segments (eg demographic for students, behavioral for long-term consumers).
Make Plans: Design a marketing plan that outlines specific tactics you plan to use, like advertising on Instagram for young shoppers.
Calculate Impact: Measure the plan’s success by, say, engagement rates or sales growth.
Example: In a BBA project example, one student surveys 60 customers, and discovers that 80% are urban students who want quick delivery. Relying on secondary data about growth of urban e-commerce, they break the market into geography and behavior in order to map a budget-friendly plan for same-day delivery promotions.
Also Check : Primary vs Secondary Data in BBA Projects: Using SWOT Analysis for Stronger Reports
Internship Application: An intern at an e-commerce enterprise could segment their customers by location, allowing them to drive conversions in metro areas by targeting those with premium subscriptions using geographic-specific information.
Addressing Common Challenges in Market Segmentation
Scanty Data: Small sizes of samples (such as collecting nly 20 customers in a survey) can be an obstacle to segmentation. Solution: Pair smaller surveys with secondary sources, such as free industry reports or government data, to confirm results.
Overestimating the demand: Students may overestimate what they think a customer might be into (e.g., assuming all young adults prefer luxury products). Solution: We already know people are playing in different ways. Cross-reference primary evidence with secondary-level trends, such as reports on youth spending habits.
Resource Limitations: Time or the availability of data can be constraining. Solution: Have available resources such as Google Forms for speedy polls and tap into open online databases.
Market Over-Segmentation: Market size may be too diluted if there are too many segments. Solution: Choose the 2-3 dimensions that are conferring more valuable insights and clarity in your data –for example, age and location–.
Example: A student with a data limit surveys 40 customers (80% like eco-friendly) and identifies sustainable trends within a book report to segment by psychographics using an extreme angle on green-minded shopping.
Key Challenges and Solutions Table:
| Challenge | Solution | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Data | Use surveys and secondary sources | Survey 30 customers + industry reports |
| Data Misinterpretation | Cross-check with trends | Validate survey with market reports |
| Resource Constraints | Leverage free tools | Use Google Forms for quick data |
| Over-Segmentation | Focus on key segments | Target students and urban areas only |
Exam Tip: Discuss challenges and solutions in descriptive answers to demonstrate critical thinking.
FAQs on Market Segmentation
What is Market Segmentation and Why is it important for BBA students?
Market Segmentation – Segmenting, is used to breakup a market into smaller groups of customers that have similar needs. For BBA students to be successful in projects, exams and internships they must design campaigns that clearly speak to the target audience.
How will Market Segmentation help me in getting good Grades in my marketing project?
Through Market Segmentation, this will enable students to access some of their targeted campaigns (eg From promoting budget products to students) Applied Understanding low yields the desiredResults.
What are the major Market Segmentation types?
They are Demographic (age, income), Geographic (location), Psychographic (lifestyle, values) and Behavioral (buying habits).
How can I utilize Market Segmentation in internships?
Analyze customer data through segmentation and to figure out the right strategies for your customers, such as offering a service specifically to urban people using geographic segmentation.
Conclusion
One essential quality that BBA students lack is Market Segmentation, But it will spare no one to help students develop this market segmentation and they can secure good grades in academic projects, exams & internships. However, by learning its fundamental concepts, related methods and tactics to overcome obstacles, they will be capable of crafting effective campaigns as well as getting ready for competitive marketing careers. This guide can help you excel at Market Segmentation and improve your BBA course performance by establishing a solid foundation of Strategic Marketing.
What is Green Marketing? A Guide for Marketing Students
👨💼 Author: BBAProject Editorial Team
✍️ The BBAProject Editorial Team comprises business graduates and educators dedicated to creating practical, syllabus-based learning resources for BBA students.
⚠️ Please Note: Articles published on BBAProject.in are well-researched and regularly updated. However, students are advised to verify data, statistics, or references before using them for academic submissions.