Importance of Business Law: Every decision-making process, including the selling of a product and the closing of a contract, hinges on the legal framework known as Business Law. Alongside Business Law, each form of business practice should observe the fairness, ethics, and legality of the consequences of the decisions made.
Each management and business student should understand the significance of the business law. This would enhance decision-making capacity, promote the avoidance of conflicts, and the construction of solid, amicable business partnerships. This is a simple and practical explanation of the primary concepts of business law, the offer, the consideration, and the predominant sources of business law, as you would explain it in class, with a teacher who is a friend.
What is Business Law?
Business Law is a branch of law, also known as Commercial or Corporate Law, which pertains to the rules and regulations covering the governance of businesses and the transactions involved in trade and commerce. It also outlines the business formation processes, contract creation, selling of goods and services, and the mechanisms of conflict resolution.
Simply put, business law makes sure all commercial activities are conducted fairly, legally, and orderly. It also safeguards businesses against legal threats, as well as consumers, employees, and investors against abusive practices.
Business law comprises:
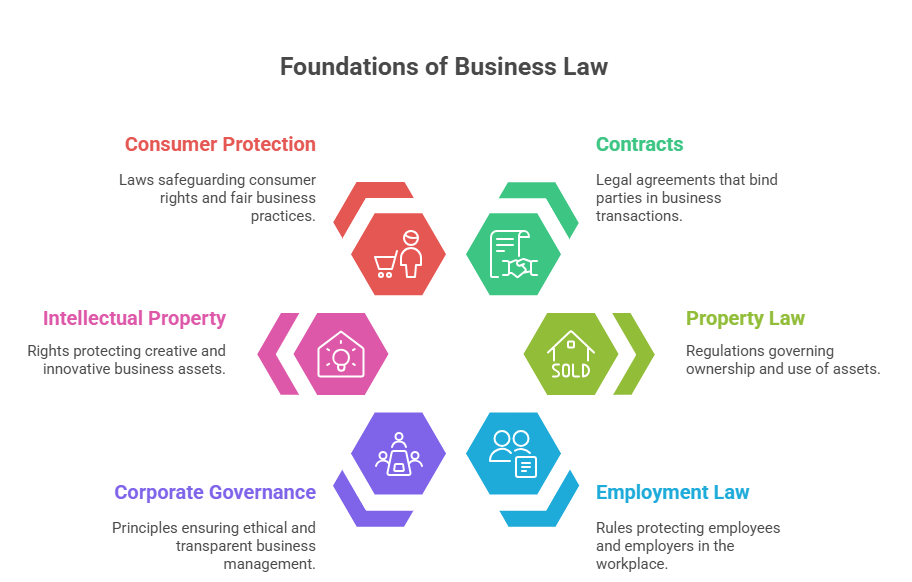
Contract Law – oversees agreements, offers, and consideration.
Company Law – governs the formation and management of companies.
Consumer Law – entails the protection of consumer rights.
Employment Law – concerns wages, working conditions, and employee rights.
Sale of Goods Act – regulates the buying and selling of goods.
Importance of Business Law
The impact business law has on the operation of businesses and business activities explains its importance. It does not matter if the business is a small startup, a global corporation, or anything in between – business law is always instrumental in upholding discipline, preventing fraud, and promoting equity.
Establishes a Legal Framework
Business law establishes a legally permitted range of operations for each business. It outlines what is legal and illegal, thereby guiding business owners in their decisions. For example, buyers are protected under contract law and can sue if a seller does not deliver goods as promised.
Promotes Fairness and Transparency
Ensures that everyone involved in a business transaction is treated justly. There are laws such as the Consumer Protection Acts that defend customers against fraudulent advertising and defective products. There are also laws that require companies to be transparent in their financial reporting.
Protects Rights and Interests
Business laws also protects the interests of stakeholders with all their layers – the owners, the employees, the consumers, and even the society as a whole. It protects against the abuse of power by big corporations, and makes sure that there is competitive fairness in the market.
Prevents and Resolves Disputes
Business law diminishes the likelihood of implementation of conflicts by specifying the way in which disagreements are to be legally settled. For instance, in a disagreement between the two companies about the terms of payment, they can refer to the contract and the law which saves them from unfair means to deal with the issue.
Encourages Ethical Practices
The purpose of such legal regulations is to motivate a business to comply with the law, to be ethical, and to pay taxes without malice in a way that discourages exploitation of the public and corruption. It encourages trust between the business and the client.
Supports Economic Growth
Legal order and compliance encourages business which, in turn, leads to economic growth. Strong legal systems with order discourage law breaking in business and takes a positive outlook towards foreign investments which will stimulate development of the economy and provide a business with a positive and stable environment.
In conclusion, compliance with business laws stimulates the order of economic activity to be innovative and to also invite investment.
Definition of Offer in Business Law
In the realm of business and contract law, an “offer” is one of the core constituent elements of a contract. Without an offer, a contract cannot come into existence.
In the Indian Contract Act, 1872 at Section 2(a) states:
“When one person signifies to another his willingness to do or abstain from doing anything with a view to obtaining the assent of that other to such act or abstinence, he is said to make a proposal (offer).”
In other words, an offer is a definitive expression by one individual to another, of a willingness to contract, on specified terms, proposing the other party’s assent.
Example:
If Ramesh tells Suresh, “I am willing to sell my car for ₹3,00,000,” that is a legal offer. An acceptance by Suresh would mean the formation of a contract.
Essential Elements of a Valid Offer
Clear Communication: The offer must be communicated to the person to whom it is being made. An offer that has not been communicated is of no legal consequence.
Intention to Create Legal Relations: The offer conveys the intention of the parties to create a contract and not a mere social or domestic arrangement.
Definiteness: An offer must be clear and detailed. If the offer contains uncertainty, it will not be valid.
Offer versus Invitation to Offer: A display of goods in a shop is not an offer; it is an invitation to customers to make an offer.
Real-Life Example:
When a company advertises a job position, it is not making an offer, but it is inviting applications. The actual offer is made when the company selects a candidate and issues an appointment letter.
Knowing the definition of offer in business law allows students to determine if a business proposal is legally binding.
Definition of Consideration in Business Law
When an offer is made and accepted, the parties must exchange something of value. This is known as “consideration,” and is the basis for every contract.
In the Indian Contract Act, 1872, under Section 2(d) it is stated that:
“Consideration is defined as something that has been, or is promised to be, done, at the request of the promisor, by the promisee or any other person.”
In other words, consideration is any act or promise to do something that is to be done to the other party. For every promise made, there must be something of value. This can be money, services, goods, or even a promise to do something or to refrain from doing something.
Take the following example:
Ananya has been offered a payment of ₹10,000 to design a company logo. While the payment is a consideration, the service to be rendered is also a consideration.
Consideration must be valid to be acceptable legally.
It must be done at the promisor’s request.
It can be from the promisee and any other individual.
It can be done in the past, be done in the present, or be promised for the future.
It must be real and not imaginary.
It must be lawful and morality shouldn’t overshadow legality.
Also Read : Understanding Valid Contracts and Types of Contracts Under the Indian Contract Act
Consideration legality can be explained by:
In the case of Currie v. Misa (1875) case, the Court defined consideration as a right or interest that a party has, a benefit or profit, or any form of forbearance a party directly or indirectly sacrifices, or a responsibility that a party must take up.
To summarize, consideration in business law means that every contract has an element of quid pro quo and is not just a unilateral promise.
Sources of Business Law
Business law has originated and evolved from various laws, customs, and court rulings over the years and not just from one single source. Tracing the sources of business law will show how the various legal principles evolved over time.
Legislation (Statutory Law):
This is the most vital and primary source. The business laws of the country are primarily based on acts passed by Parliament or State Legislatures.
As an example, one can refer to the Indian Contract Act, 1872; the Companies Act, 2013; or the Sale of Goods Act, 1930.
Judicial Decisions (Case Law):
Courts apply and interpret laws, which leads to the creation of binding legal precedents. For instance, Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball Co. (1893) is a key case that explains how advertisements can sometimes be construed to be a valid offer.
Customs and Trade Usages:
Certain business customs that are accepted over time greatly shape business practices. For instance, in the textile or diamond industries, traditional trade customs greatly influence how contracts and payments are structured.
English Mercantile Law:
Since the British legal system greatly influenced Indian law, several principles of English Mercantile Law continue to be incorporated into Indian business law.
Equity Principles:
These consist of the moral principles created to guarantee the compassion and justice needed when rigid legal guidelines may inflict unnecessary suffering.
International Treaties and Conventions:
With the rise of globalization, the new sources of business law, as well as foreign trade agreements and regulations, encompass international laws and business treaties such as WTO agreements.
The Practical Importance for Students and Professionals
For BBA students, knowing business law is more than a theoretical requirement, as it also prepares them to think about responsible management. Understanding the principles of business law assists in contract management, recognition of employee rights, customer interaction, legal compliance, and government regulation.
For entrepreneurs, it boosts confidence in conducting business and legal control while preventing loss and risks, building reputation, and enabling safe operations.
FAQs related to Business Law
Why is business law important for students?
It allows them to learn about the legal functioning of the corporate world; this helps minimize risks and enhances the quality of decision making.
What is the definition of offer in business law?
An offer is the term given to a proposal made by one person to another to create a legal contract under specified conditions.
What is the definition of consideration in business law?
Consideration is one of the fundamental elements of a contract and involves the exchange of value between parties, which can be money, goods, or services.
What are the main sources of business law?
It comprises legislation, judicial decisions, customs, English law, equity, and international conventions.
How does business law help in business growth?
It instills confidence, minimizes disputes, and ensures that the business operations are conducted in a fair and orderly manner.
Conclusion
Business law is immensely important and cannot be taken lightly. It guarantees that every step involved in any legal business activity is fair and predictable. Including the definition of offer and consideration in the contract law’s basics and the sources of business law showcase how the principles of business law have developed over time.
To students, entrepreneurs and professional peers alike, since it it the law governing the economic and business environment, it is essential to be able to understand and make legally sound, rational, equitable and ethical decisions in order to develop and maintain constructive and morally upright business relations.
👨💼 Author: BBAProject Editorial Team
✍️ The BBAProject Editorial Team comprises business graduates and educators dedicated to creating practical, syllabus-based learning resources for BBA students.
⚠️ Please Note: Articles published on BBAProject.in are well-researched and regularly updated. However, students are advised to verify data, statistics, or references before using them for academic submissions.

