In business, every organization has to handle a collection of different products, services, or units, and not just a single one. Some of these may be highly profitable, some may be growing, and others may require a complete restructuring. Balancing these all together requires a portfolio strategy in strategic management.
Business leaders, just like any other investors, manage a portfolio, except here it is a portfolio of business units. The objective is to ensure all the resources, time, and energy of an organization is put to best use to achieve growth in the long run.
For Business students, grasping portfolio strategy in strategic management is important, not just because of its theoretical aspect, but its practical application in real corporate decision-making. It encompasses the entire spectrum of corporate diversification, resource allocation, and sustaining competitive advantage.
What is Portfolio Strategy in Strategic Management?
A portfolio strategy in strategic management pertains to the evaluation, control, and optimization of the array of business units or products offered in a company.
It addresses top management concerning the decision of:
Which ones to invest in,
Which ones to maintain, grow, or dispose of, and
Which ones to keep.
An organization portfolio strategy identifies how resources are spread to ensure efficiency and profitability across the whole organization.
Consider a conglomerate that owns businesses across different sectors e.g. manufacturing, services, and technology. They will need to apply portfolio strategy to understand how to advise and divide resource allocation across the sectors, focusing on profitability, market dynamics, and potential growth.
The Role of Portfolio Strategy in Strategic Management
The role of portfolio strategy in strategic management is to strike a balance between growth and stability. It ensures that an organization cannot depend on a single business line to survive.
Here’s how it functions:
Resource Allocation:
Identifying the business units that are likely to perform well.
Risk Exposure:
Spreading market risk through different products.
Strategic Alignment:
All business units help in achieving the desired organizational goal.
Performance Management:
Identifying which of the businesses is underperforming in order to restructure, exit, or liquidate.
Sustainable Growth:
With a balanced portfolio, the company can position itself in a way to counter challenges and negative changes.
The bottom line is that the best portfolio strategy in strategic management is to ensure the organization preserves directional clarity and structural integrity.
Levels of Strategy and the Role of Portfolio Strategy
Within the realm of strategic management, decisions take place on three levels:
Corporate, Business, and Functional.
The portfolio strategy pertains to the corporate level, wherein management addresses issues of diversification, mergers, acquisitions, and divestments.
At this juncture, management asks:
In which industries should we compete?
How much should we allocate to each strategic business unit?
Should we take on new businesses or divest from existing ones?
The portfolio strategy in strategic management answers these and other.. management questions ensuring that the corporate strategy aligns with the overall long-term goals of the business.
Key Components of Portfolio Strategy
Well crafted portfolio strategy in strategic management has a number of these core components and helps illustrate the connection between theory and practical corporate management to students.
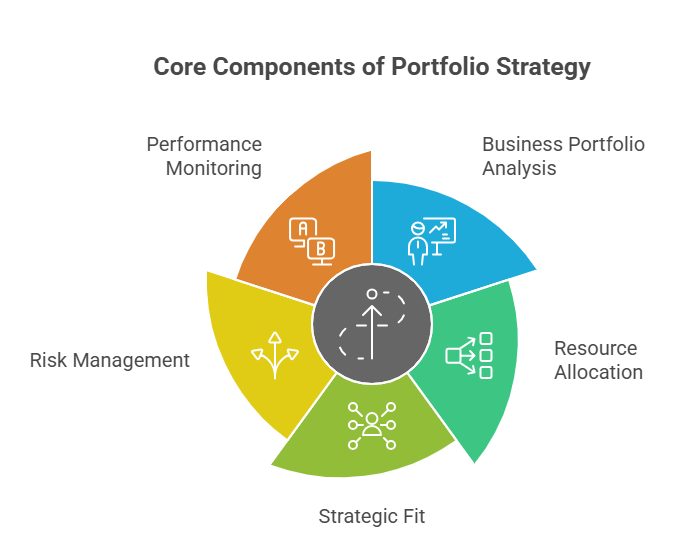
Business Portfolio Analysis
This is the starting point of portfolio strategy. It entails assessing the performance and growth potential of each business unit. By examining market growth, profitability, and market share, management determines the investment and divestment priorities.
Resource Allocation
Resources, whether time, money, human, or technological, are finite. Portfolio strategy determines the optimal allocation of these to business units, in order to maximize total organizational returns.
Strategic Fit
Different businesses under the same corporate umbrella should support each other. For example, one business could supply raw materials to another, thereby creating synergy and saving costs.
Risk Management
With diversification, a firm can minimize its reliance on a single product or market. This creates more stability within the overall portfolio, even when one unit is not performing well.
Performance Monitoring
Consistently reviewing the performance of each portfolio enables the firm to respond to market changes swiftly and replace underperforming units with more profitable ones.
Approaches to Portfolio Strategy
Organizations vary in design and management of their portfolios. A few of the more common frameworks in the field of strategic management include:
BCG Growth-Share Matrix
One of the most common tools for portfolio management analysis is the BCG Matrix. It rates business units by the growth of the market and the market share. It categorizes units into:
| Category | Description | Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Stars | High growth, high market share | Invest and grow |
| Cash Cows | Low growth, high share | Maintain and harvest |
| Question Marks | High growth, low share | Analyze and decide |
| Dogs | Low growth, low share | Divest or exit |
This model helps companies visualize where to invest and where to cut losses — an essential step in portfolio strategy in strategic management.
GE McKinsey Matrix
This matrix expands the BCG model by including the business strength and the industry attractiveness. This helps management assess multiple business units more accurately.
Life Cycle Approach
In this approach, portfolio management is based on the stage of the business. It can be at the introductory, growth, maturity, and decline phase. The focus is to have a balanced portfolio with a mix of growing and stable units.
Portfolio Strategy in Diversified Companies
In diversified companies, how portfolio strategy is applied influences success in the long run. Within the scope of multiple lines of business, the challenge is how best to balance areas of rapid growth with stable, more predictable, and mature cash sources.
As an example, one division of a corporation may be a steady cash earner while another is a more risky business focusing on the highly dynamic and innovative new tech. A well-designed portfolio strategy allows the stable cash-earning division to fund development in the risky-and-volatile new tech division.
This allows a corporation to innovate while still maintaining business viability. This concept and strategy is a must learn for every corporate strategy manager.
Understanding the Importance of Business Law: Offer, Consideration, and Sources Explained Simply
Steps in Developing a Portfolio Strategy
In strategic management, developing portfolio strategy requires a number of critical steps.
Environmental and Internal Analysis Inputs:
Capacities and competencies must be aligned with prevailing market conditions. This is required for identifying capabilities, opportunities, and possible threats.
Identify Business Units:
Identify and demarcate strategic business units (SBUs) on the basis of products, markets, or clientele.
Evaluate Each Unit:
Look to employ performance and potential matrices like BCG or GE, and/or others.
Decide Investment Priorities:
Decide strategic priority and the extent of resources – capital, people, or tech – that will be allocated.
Develop Synergy and Balance:
This implies that all units must be aligned to support one another synergistically and in the scope of financial resources.
Monitor and Review:
Continuously observing changes ensures current and future relevancy of the portfolio.
For this reason, management achieves a portfolio that is dynamic, flexible, and responsive to the changes balanced to incorporate the differing market realities.
Benefits of Effective Portfolio Strategy
Benefits from strategic management arise from effective portfolio strategies.
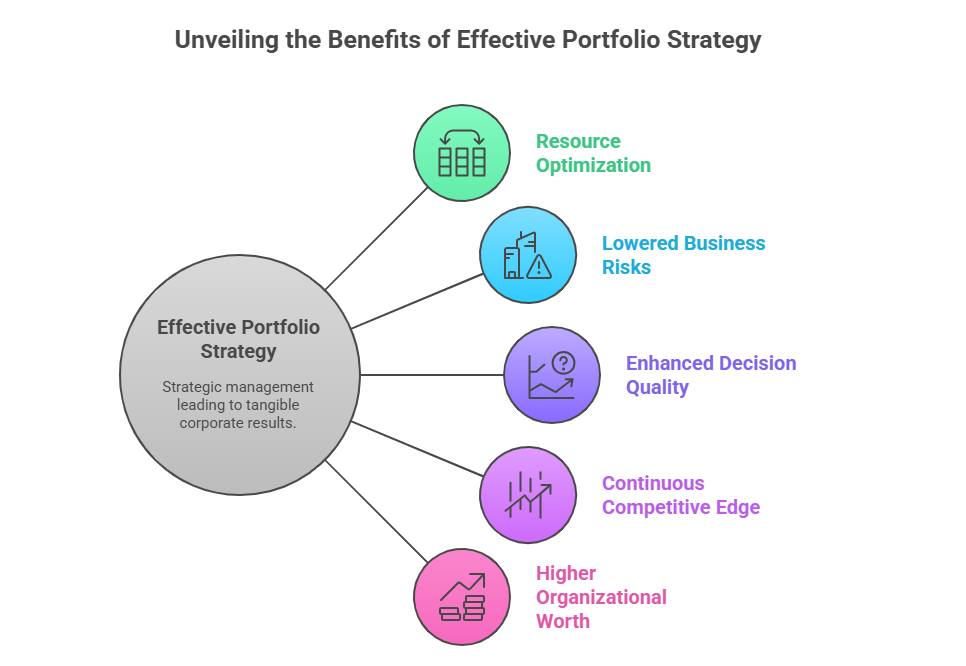
Resource Optimization: Ensures that the available monetary and the physical efforts are channeled to areas that are eventually profitable.
Lowered Business Risks: Risks from market overexposure are minimized through diversification.
Enhanced Decision Quality: The overall operational view across the different units of a business is provided to the management.
Continuous Competitive Edge: The balance achieved strategically, fosters sustained growth for the business.
Higher Organizational Worth: Corporate valuation is improved through effective portfolio management.
In essence, it is the final outcome that shifts the strategy from being a mere plan to tangible results achieved at the corporate level.
Hurdles in Portfolio Strategy
Most of the time, challenges that accompany strategic management will not leave portfolio management untouched.
Interdepartmental Design: Juggling the competing priorities of diverse business units can become overwhelming.
Tactical Resource Allocation: Scarce resources will always force the management to make tough compromise.
Economic Variability: The changes in the economy will directly affect portfolio performance.
Strategic Disconnect: Some business units may inherently be misaligned with the overall aims of the firm.
Cognitive Distortion: Business managers may get fixated, thus refuse to abandon poorly performing units even when they are unprofitable.
Using effective leadership to finalize data and make necessary adjustments to the portfolio is a way to mitigate unaddressed issues.
Practical Example
Consider a company with three business units: manufacturing, renewable energy, and e-commerce.
The manufacturing unit has predictable and stable cash flows.
The renewable energy unit, on the other hand, is rapidly growing but is capital hungry.
The e-commerce unit is the newest and carries a lot of uncertainty.
Adopting a portfolio approach in strategic management, the leaders would likely decide to allocate the profits from manufacturing to subsidize the growth of renewable energy, while keeping a close eye on the performance of the e-commerce unit. If e-commerce underperforms, it is likely the company would choose to divest that unit.
This is a simple example of how strategically configured corporate portfolios can develop over time and enhance the corporate value of the organization.
Conclusion
To close, portfolio management strategy in corporate planning is a vital part of value management and ensuring corporate goals alignment of all business streams.
For BBA students, understanding this concept is vital to building a career in corporate strategy, consulting, or financial management. This is a combination of analytical skills, strategic resource management, and commanding foresight within a corporate strategy. These are the traits of business leaders.
A company’s success does not rest only on how each business unit functions on its own, but how each unit functions as part of a cohesive portfolio.
FAQs About Portfolio Strategy in Strategic Management
What is portfolio strategy in strategic management?
This is the balance, profitability, and growth management of various business units within a company.
Why is portfolio strategy important?
It is important because it assists in resource allocation, risk diversification, and the alignment of various enterprises with corporate objectives.
What are common tools for portfolio analysis?
Common tools include the BCG Matrix, GE McKinsey Matrix, and Life Cycle Analysis.
How does diversification relate to portfolio strategy?
Diversification is the practice of spreading investments across various industries to reduce risk and maintain consistent returns.
What challenges occur in portfolio strategy implementation?
Common challenges include complexity of coordination, insufficient resources, and fluctuating market conditions.
👨💼 Author: BBAProject Editorial Team
✍️ The BBAProject Editorial Team comprises business graduates and educators dedicated to creating practical, syllabus-based learning resources for BBA students.
⚠️ Please Note: Articles published on BBAProject.in are well-researched and regularly updated. However, students are advised to verify data, statistics, or references before using them for academic submissions.

